You are likely familiar with industrial cooling equipment if your business must maintain a specific temperature to aid production. However, there are a few things to keep in mind if you’re new to the process.
Several types of cooling systems help to cool a processing unit or power plant. Chillers and cooling towers top the list. In both cases, a liquid needs to cool before it can act as a coolant. First, however, you should be aware of the differences between the two systems.
What are chillers and cooling towers? And which is best for my business? Our easy-to-digest guide will help you understand what these two pieces of equipment are, how they can benefit your business, and how they can work together. Have a look! Listed below are all the details you need.
What Is a Cooling Tower?
A cooling tower is a piece of specialized equipment used to cool down critical machinery and control temperatures.
It uses evaporative cooling, which involves cooling water and air to get into direct contact. So, the water that circulates inside the tower is cooled. Thus, a small amount of water evaporates through the building, lowering the circulating water’s temperature.
What Is a Chiller?
A chiller is also an industrial device that transfers heat from one place to another to regulate temperature. The chiller uses exchangers and condensers instead of the internal basin and pump used in cooling towers. Food and beverage industries, oilfield production, and metal plating processes depend on chillers to regulate temperature.
Components of Chillers and Cooling Towers
Choosing between chillers and cooling towers will require you to learn the different components that go into both.
There are only three separate components to a chiller system:
-
Compressors,
-
Evaporator heat exchangers,
-
Condenser heat exchangers.
Due to their simplicity, it is easy to identify which component is at fault if a problem occurs during the cooling process.
As a result of heat exchange, liquids are cooled effectively before being returned to industrial processes.
A cooling tower consists mainly of:
-
Pumps
-
Basin
Pumps move water throughout a cooling tower to cool the area. The pumps in the cooling tower allow the water to circulate, regardless of the type of cooling tower you use for your industrial application. Any water discharged from the cooling tower will be collected in the distribution basin.
Chillers & Cooling Towers: How Do They Work Together?
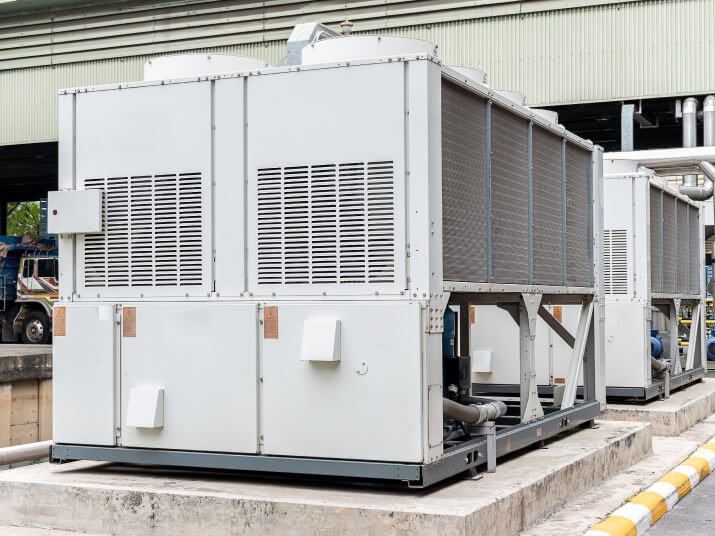

Now that we’ve covered both pieces of equipment let’s move on. In which way do a cooling tower and a chiller work together to create the perfect industrial environment?
The chiller – air or water-cooled – is placed either in the basement or on the roof of a building. The cooling tower, on the other hand, is used to capture excess heat within the structure.
Most cooling towers are located on roofs. The two units operate on a vapor absorption cycle, which removes heat from the building by using a refrigerant fluid.
With the condenser system, the evaporator and the condenser cylinder work together as a refrigerant cycle. The two water lines constantly move heat out of the evaporator without meeting before getting to the condenser. Then, as the warm water rises, it reaches the cooling tower on the roof.
Regardless of the type of cooling tower or chiller you choose to use, these systems come in a wide range of sizes. It is, therefore, possible to combine a small chiller with a similar cooling tower.
If the application or equipment is small or portable, adding a mobile cooling tower directly on top of a water-cooled or air-cooled chiller is possible. Additionally, water-cooled chillers may combine larger chillers with cooling towers.
Use-Cases of Chillers and Cooling Towers
Let’s understand the usage from a business perspective. First, using a large chiller and a large cooling tower can efficiently support a small industry or power plant. Moreover, it can save you a lot of money in the long run if you can afford the upfront costs for these two systems.
In a power plant, you can install a water-cooled chiller on the lowest floor of the building or an air-cooled chiller on the roof to create a central cooling facility.
The cooling tower must always be on top of the building to allow the heat to disperse properly.
Other Chiller Use-Cases:
-
Applications for refrigeration
-
Applications in the plastics industry
-
Microbreweries and wineries
-
Applications for metal finishing and water-jet cutting
Other Cooling Tower Use-Cases:
-
Thermal power stations
-
Oil and gas refining plants
-
Power plants that are located near rivers and lakes
-
Larger mechanical processes where high amounts of heat will be produced
Benefits of Chiller and Cooling Towers for Businesses
Do you want to learn how cooling towers and chillers can benefit your business?
Benefits of Chillers
Three primary benefits of chillers are:
1. Enormous Cooling Output: Depending on size, a chiller can offer between 180,000 and 18,000,000 BTUs of cooling per hour, making it ideal for substantial industrial buildings where regular air conditioners just cannot handle it.
2. Equipment Protection: Coolers safeguard your equipment, which is the main reason for having them. An equipment that breaks down due to overheating might cost thousands of dollars to replace, which you may not be able to afford.
3. Cost Reduction: Chillers circulate water, not pull it from a municipal source and dump it into the sewer system. This saves money on water and sewer expenses. In addition, water chillers are much more efficient than water towers in the summer and cost less to run.
Benefits of Cooling Tower
Three primary benefits of cooling tower are:
1. Industrial Cooling Efficiency: Cooling Towers can be very large and capable of removing heat from industrial setups. An industrial cooling tower is used in many refrigeration systems and can be found in power plants, chemical processing, steel mills, and many more.
2. Commercial Benefits: Commercial cooling towers can also be utilized for comfort cooling in significant commercial buildings such as airports, schools, hospitals, and hotels.
3. Cost-Effective: Machines and processes that create a lot of heat must be constantly cooled to keep them running efficiently. A cooling tower is the most efficient, effective, and cost-effective way to remove this heat.
Final Words
Cooling towers and chillers can work together for more efficient cooling, as mentioned previously.
The type of system you pick will depend on various factors, including your budget, your cooling needs, and your space. For example, chillers are typically less efficient than cooling towers if energy efficiency is essentially oversized for your company.
The bottom line is you can make informed decisions with all the insights provided above. In addition, a comprehensive CFD analysis and simulation can help identify the apt cooling equipment suitable for your business.
A professional approach and an engineering mindset guide all we do at Mechartés. We have been able to offer outcomes that our clients have been pleased with because of our advanced methodology, simulation algorithms, processing capacity, and more than 16 years of experience.
Get in touch with Mechartes today for industry-leading CFD and FEA, and other design solutions!


 Share
Share  facebook
facebook