In today’s world, where energy is becoming expensive and natural resources are depleting fast, making good use of natural venting and cooling arrangements can enhance the architectural value of construction. Therefore, architects and engineers can deploy sophisticated enhancements that use daily temperature variations, breezes, shades, and other cooling factors to reduce the building’s heat.
A private home, office building, or data center facility must be designed with aspects to aid effective thermal management. Active and passive cooling technologies have been used globally to reduce heat transfer and manage conditions within a building and construction.
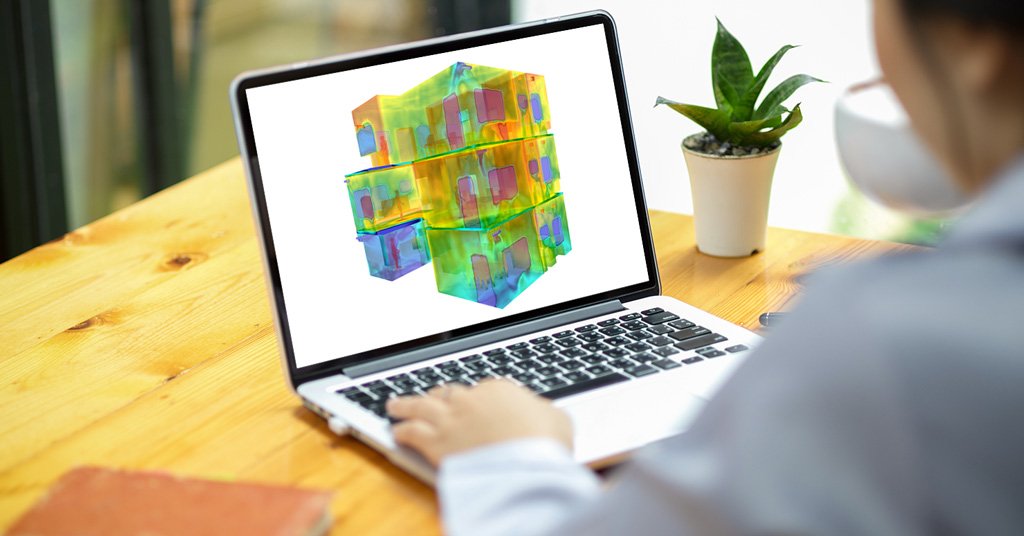
Engineers and designers use building and construction simulations to predict and analyze cooling and thermal conditions of an environment and deduce ways to exploit this natural phenomenon for thermal management of a building using either active or passive cooling.
What is Active Cooling?
In active cooling, the heat transfer effect is brought about by external devices to remove heat actively at an increased rate. For example, fans, blowers, air conditioning units, forced liquids, etc., are used as active cooling components in a building or construction.
Active cooling techniques are predominantly avoided or used only in adverse conditions as they consume extensive energy. The huge amount of energy reflects the cost of running the active cooling systems.
What is Passive Cooling?

Natural convection of heat transfer is used to effectively regulate the heat or manage the heat of a building or construction. Passive cooling techniques rely on architectural designs of natural resources like wind, soil, water, etc., to create a heat sink or heat spreaders to absorb or dissipate the heat.
This method employs the least energy or electricity consumption, thereby being friendly to the environment and saving a lot of money compared to active cooling techniques. In addition, other structures like heat pipes or thermal interface materials are used in passive cooling to maintain optimal operating.
There are several benefits to using passive cooling in buildings and construction simulations to evaluate the system’s effectiveness.
Advantages of Passive Cooling in Building and Construction Simulations
Here are five advantages of passive cooling in buildings and constructions:
1. Minimize and isolate internal heat
In manufacturing facilities or data centers where the operating equipment generates heat, the temperatures are constantly high. Therefore, using active cooling methods can cost a lot and consume a lot of electricity.
In this case, passive cooling can be used to minimize the heat or isolate the internal heat of the system to maintain optimal operating conditions in the facility.
2. Ventilation
Ventilation is an integral part of maintaining optimal temperatures in a building. Adequate ventilation is required to manage airflow and facilitate hot and cold air circulation.
Fans, blowers, and heat sinks can passively move the air around to circulate cold air inside the building and pass the hot air outside the premises.
By monitoring the air temperature inside and outside the building, fans and blowers can be strategically placed to provide ventilation and manage heat transfer.
3. Eliminate heat and provide insulation
Infrared radiation is the primary source of heat generation for a building. Therefore, keeping the rays away from a structure can help keep temperatures inside lower than the external temperatures.
Insulating the buildings can be done by creating thicker walls to prevent rays from entering the building. Light-colored walls, for instance, can also help reflect a considerable amount of infrared rays away from the building’s interior. These are some simple ways passive cooling can help eliminate the heat by providing insulation to the building.
4. Heat radiation
Passive cooling methods can also carry heat to the roof and use it as a heat exchanger by radiating the heat to the external environment.
During the day, the roof of the building is designed to keep the building cool. Ceiling fans or blowers act as a heat transfer aid and help keep the building cool by transferring the heat onto the roof.
5. Energy and cost-efficiency
Passive cooling uses lesser energy which ultimately reduces the cost needed to regulate the heat of building construction. By ensuring that the temperature of a building is maintained at optimal levels with just simple, passive design, buildings and constructions can be environment-friendly and can help save a lot of money both during installations and during future operations.
Building and Construction Simulations with Passive Cooling Systems
The heat sinks, heat spreaders, heat pipes, etc., are virtually tested using sophisticated software for viability and effectiveness during the design phase. In addition, early-thermal simulations can help builders and engineers analyze the design without needing a physical prototype.
Simulation significantly reduces costs in the design process and helps make informed decisions and implement the best passive cooling from the building and construction simulations.
When deciding between active or passive cooling for your building or construction, it is better to evaluate the cooling requirements of your building before deciding on the cooling methods.
Passive cooling has various advantages for thermal management. With adequate planning alongside building and construction simulations, you can deduce the right methods and techniques to maintain optimal thermal conditions for your building.
Mechartes’ simulation experts can help you create virtual simulations and prototypes during the design stage to help you analyze, evaluate and decide on the passive cooling for your building based on the thermal requirements.
Be it a private home, office building, data center, or industrial facility, Mechartes’ team of experienced engineers and simulation experts can help you digitally envision and simulate the actual project and dramatically enhance its thermal management solutions.


 Share
Share  facebook
facebook