Introduction
An efficient and reliable water utility service is crucial, especially in industrial areas where uninterrupted service is essential. The seawater intake facility provides critical cooling water through a 7 km network. With the current manifold deteriorating due to corrosive chlorinated seawater, a new, durable design is needed to maintain performance.
This study focuses on the root cause analysis that was carried out using numerical analysis to identify the current performance of the manifold. A combination of Fluid Dynamics Analysis (CFD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was employed to simulate and examine various scenarios to guarantee optimum design and operational safety.
Objective
This case study evaluates the surge analysis and design verification of a Seawater Intake Pumping Station, with a focus on the GRP piping design arrangement. The goal is to ensure the system’s reliability and structural integrity under various operational scenarios.
The project involved the following:
- Surge Analysis was carried out to analyze transient pressure fluctuations due to pump operations, including potential water hammer effects on the GRP piping.
- Review the GRP piping design to confirm compliance with industry standards and project requirements.
- Vibration Analysis was carried out to evaluate vibration levels within the system and identify potential resonance issues.
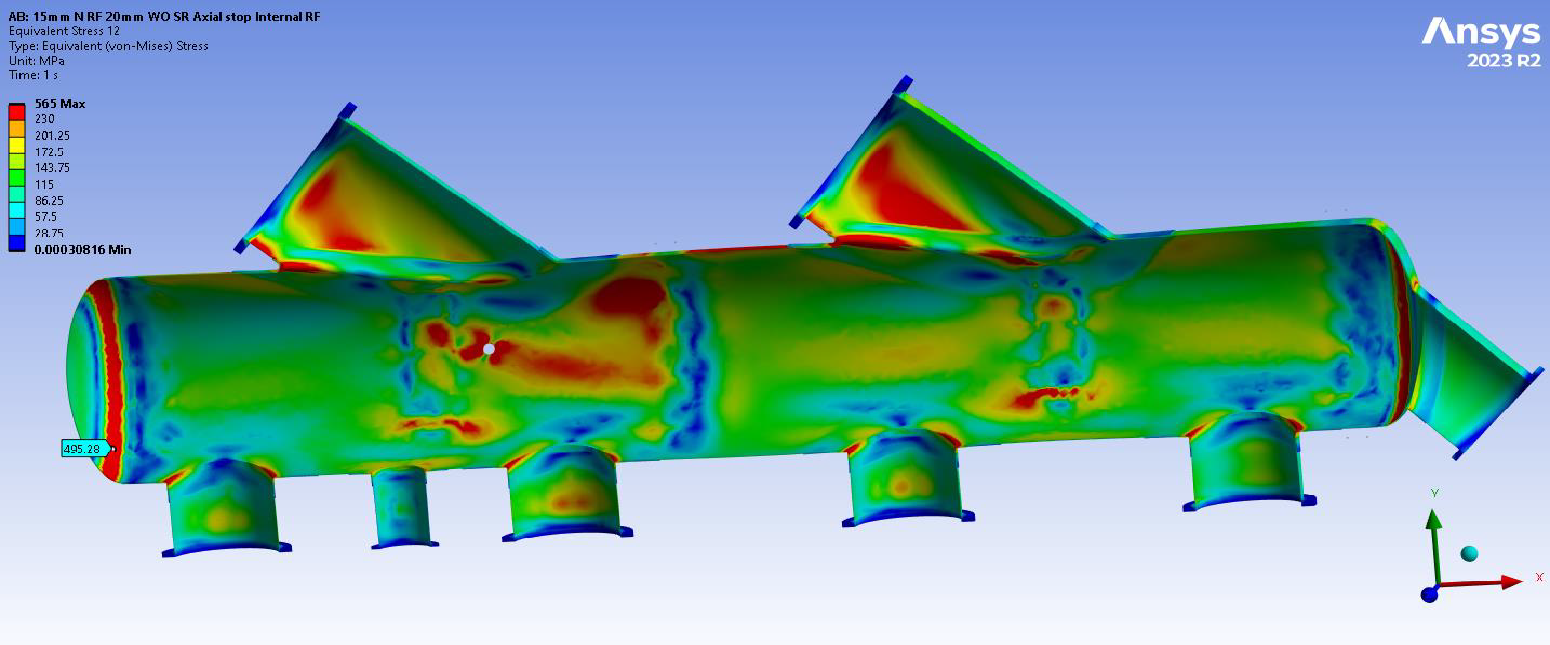
- Stress Analysis was carried out on key piping components to ensure stresses remain within acceptable limits.
- Structural Integrity Analysis to assess the structural integrity of the pumping station and its supporting structures.
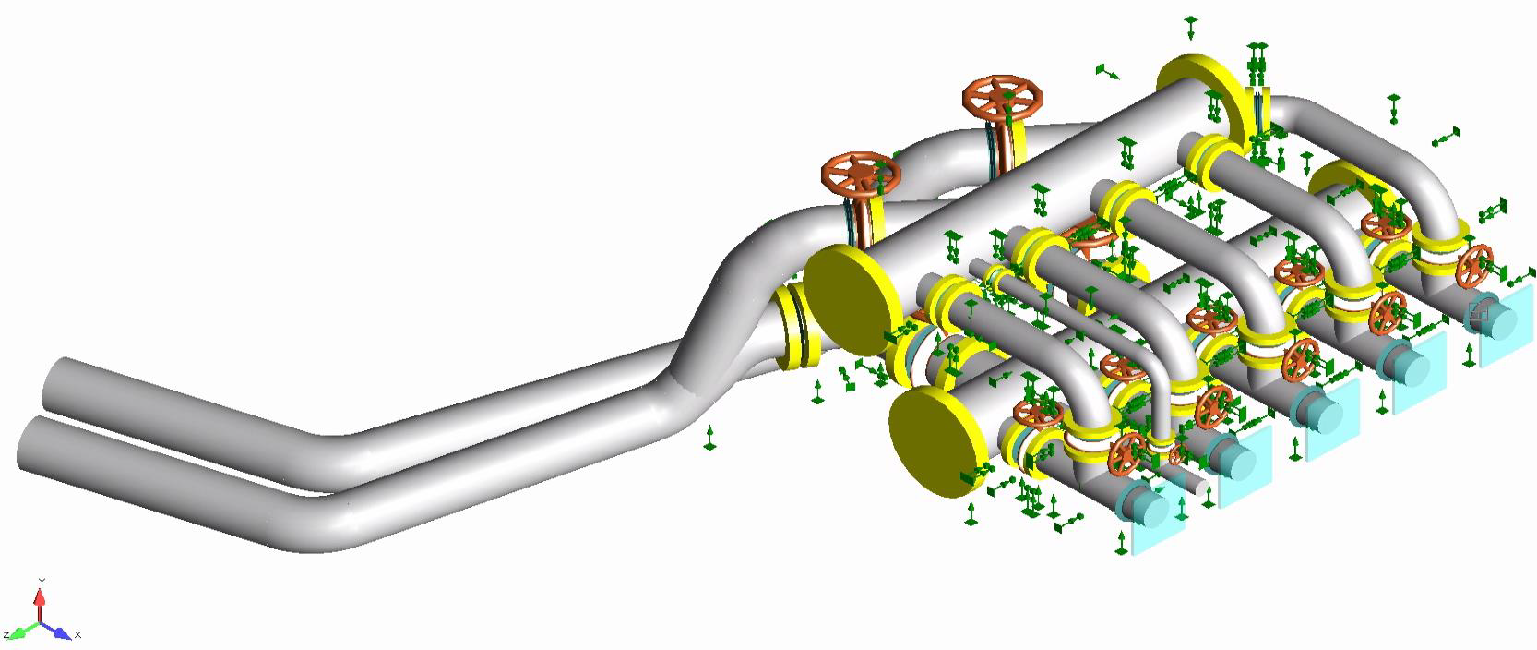
- Support and Loading Assessment to evaluate the adequacy of pipe supports and their ability to handle operational loads.
Modeling and Analysis
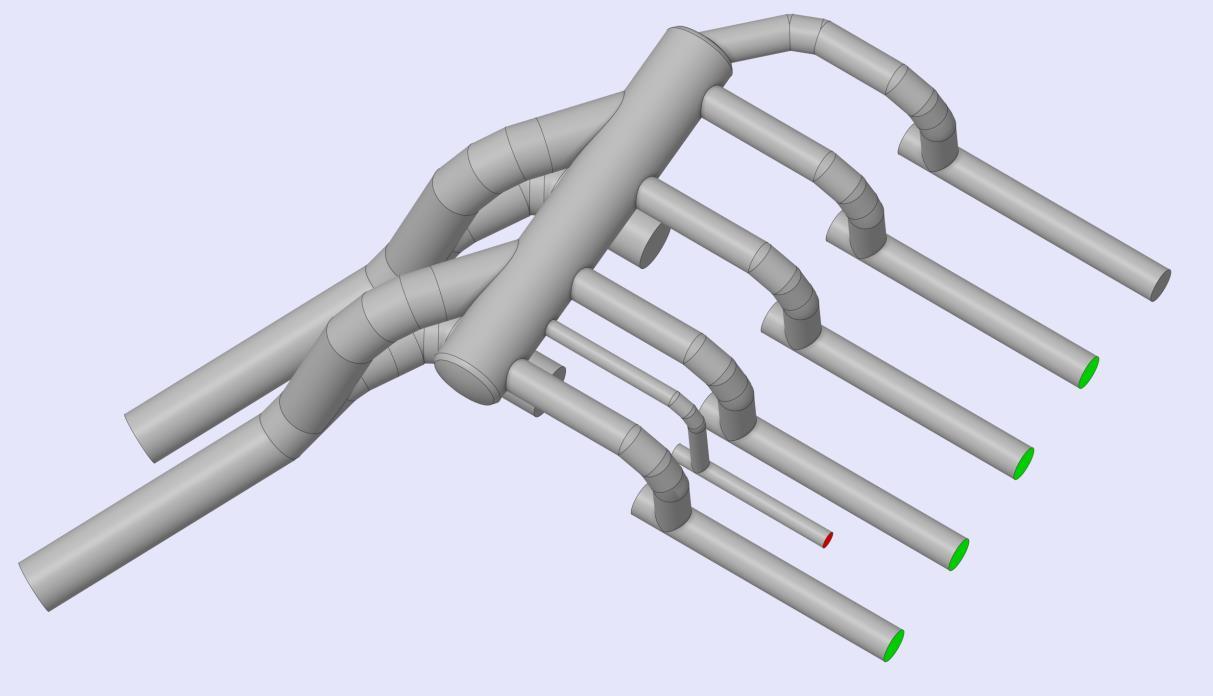
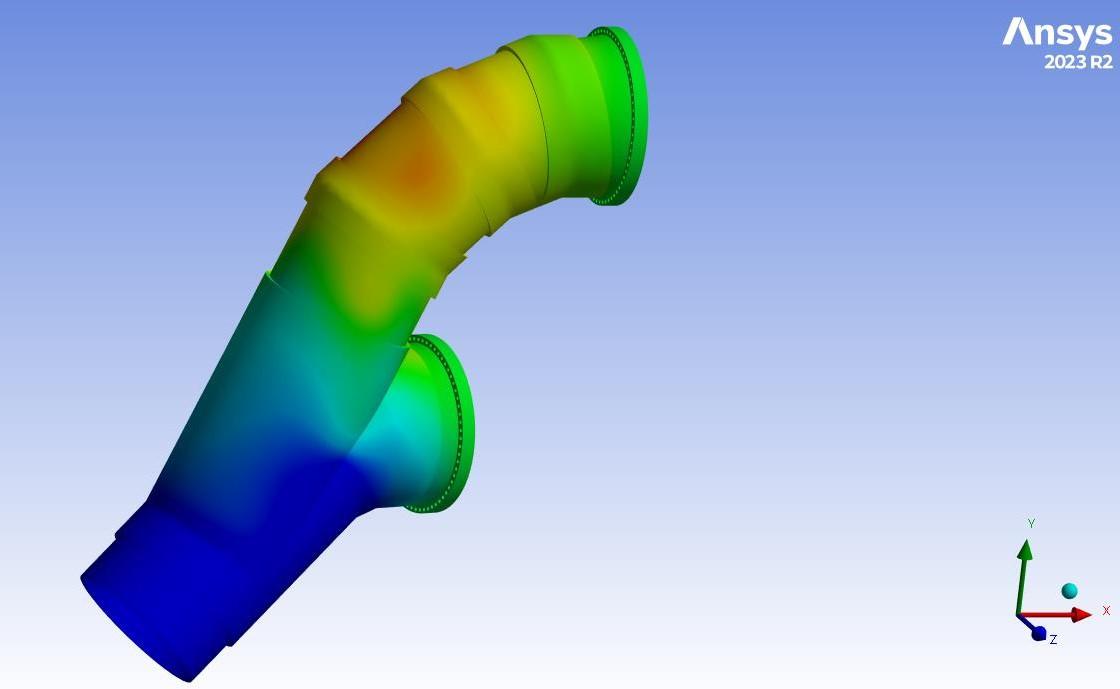
A detailed 3D model of the pumping station, including all relevant components, based on the drawings and the dimensions were developed. Finite Element analysis to assess the structural integrity of the GRP piping and support structures was carried out including evaluation of stress distribution, deformation, and load-bearing capacity under various operating conditions.
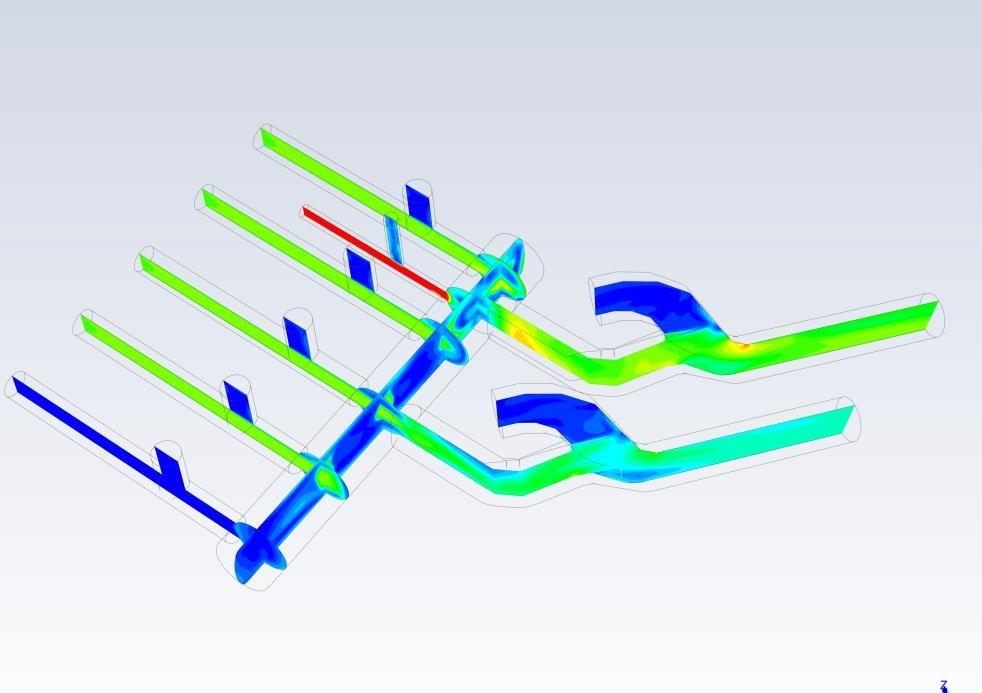
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations were carried out to study the flow characteristics within the piping system. This included assessing flow distribution, velocity profiles, and potential areas of turbulence or stagnation that could impact system performance.
Conclusion
In the project, various numerical analysis tools were used to address the immediate concerns to ensure that the future operation of the seawater intake facility meets the highest standards of reliability and efficiency.
Various numerical analysis tools including CFD Analysis, FEA Analysis, Surge Analysis, and Vibration, and Stress Analysis tools were used to evaluate the performance of the manifold. Appropriate recommendations were provided to enhance the system’s reliability, focusing on areas identified during the surge analysis, structural design verification, and flow dynamics assessments.