Objective
The 351′-00” High Shiva Statue is the “World’s largest statue of Lord Shiva” is being built in Ganesh Tekri area of the Nathdwara, Rajasthan, India. The statue will be made from concrete & cement and the void area of statue is designed with natural ventilation system since few intermediate levels of void area of statue are accessible to general public. The CFD analysis were carried out to evaluate the designed natural ventilation system efficiency during day to day ventilation & smoke ventilation modes.
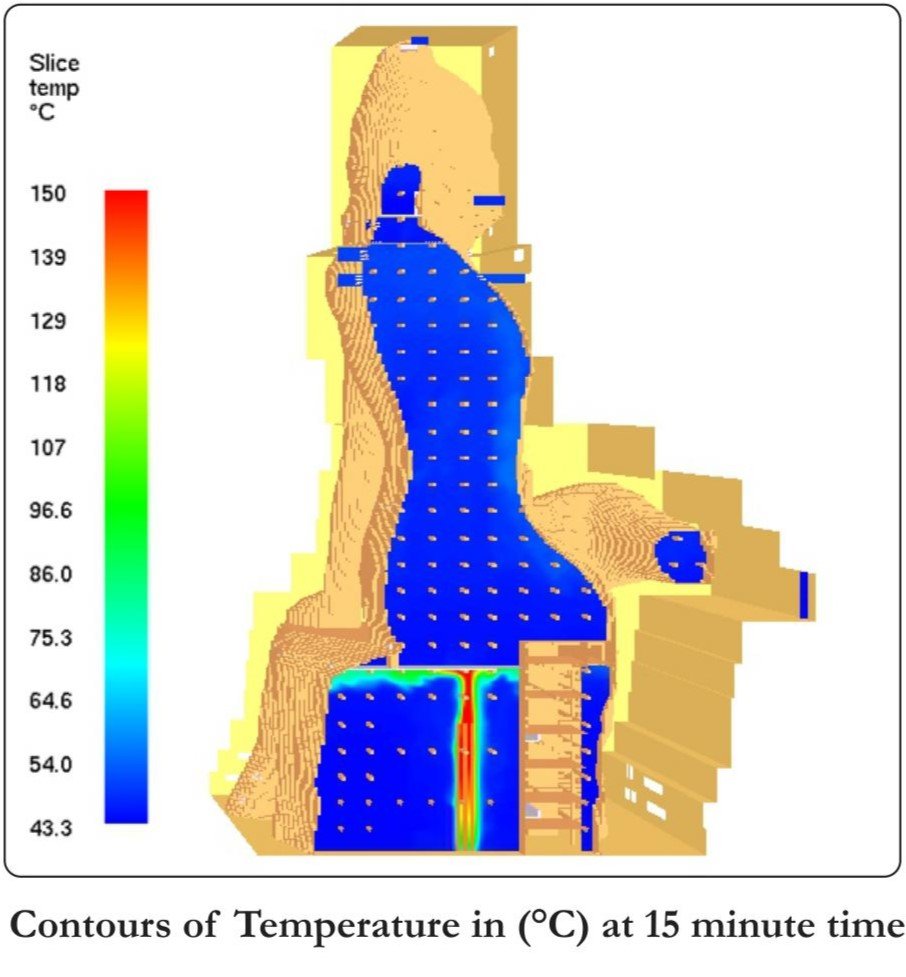
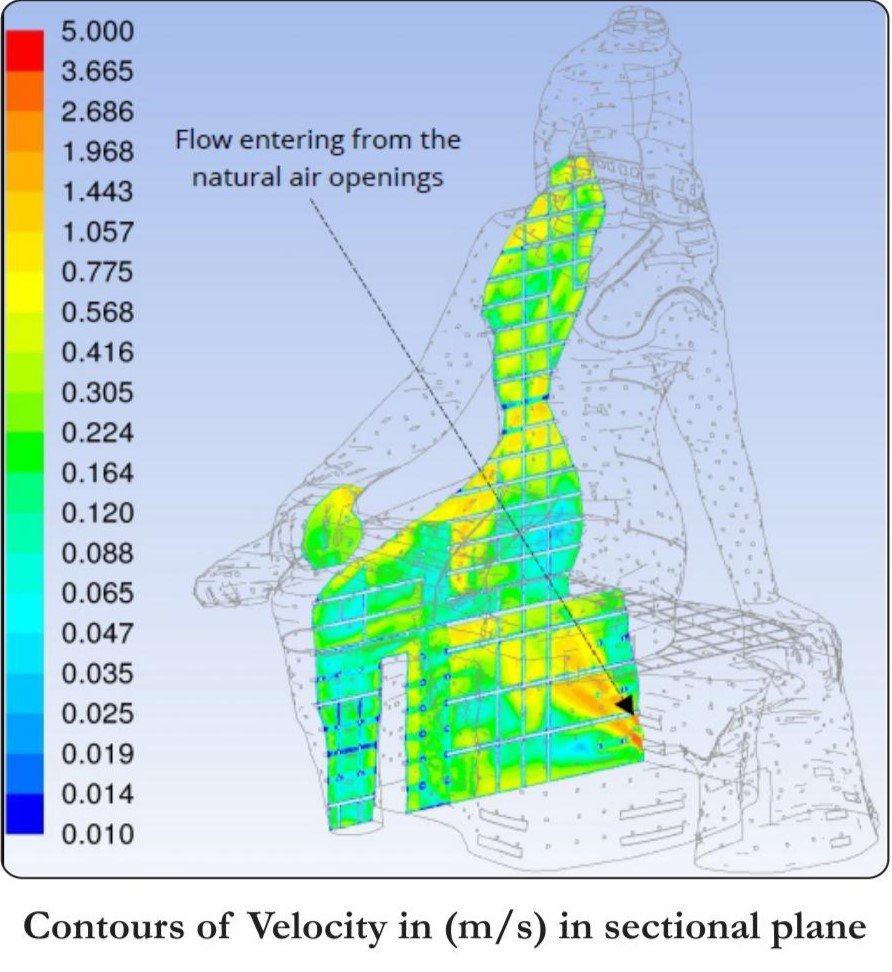
The CFD analysis for Day to Day Ventilation Mode is carried out to confirm that the designed natural ventilation system is able to maintain the proper velocity profiles such that the heat builtup is limited and there is no high temperatures within the void region for safety of structure as well as comfort of occupants.

The CFD analysis for Smoke Ventilation Mode is carried out to confirm that the escape routes of the floors that are occupied by general public are free of smoke in case of accidental fire so that occupants can escape safely. So in order to evaluate the natural ventilation system efficiency the parameters such as smoke movement, temperature & visibility profiles inside the void areas of Shiva Statue were studied .

Modeling and Analysis
The 3D model of the void areas located inside the statue from 40′ level till 351′ level of “351′-00” High Shiva Statue” was modeled including structural obstructions and the natural ventilation system louver openings. After preparing the 3D model of the geometry, the fluid domain mesh was prepared with hexagonal mesh and total 11.3 million mesh cells were generated to solve the Navier—Stokes equations for both day to day & smoke ventilation modes.
The natural ventilation system in the void area was designed by providing the louver openings at various levels and these louver openings were having 60% free area. The loud er openings provided at low levels would majorly act as air entry into the void area & the louver openings provided at high levels would majorly act as air exit from the void area.
The stead state CFD analysis was carried out to verify the velocity & temperature profiles by considering the wall material thermal properties and heat loads during the peak summer condition to calculate the heat transfer into the void area.
The transient CFD fire/smoke simulation was carried out for the period of 120 minutes (2 hours) to verify the smoke distribution, temperature & visibility profiles during the accidental cable fire scenario with 2MW fire size.

Conclusion
In normal day to day ventilation mode it was observed that the temperature profiles obtained indicating that the most of the regions of the occupancy doors are not having the very high increase in the temperature and the increase in temperature is limited to 3.2 C for the given summer ambient temperature of 43.3 C which is acceptable as per the design specifications.
During the fire/smoke ventilation mode it was observed that smoke was filled in the void area from 90’ level till 351’ level & the low levels from 40’ to 80’ levels are free of smoke for the complete duration of fire for safe escape of occupants.
lt is concluded that the natural ventilation louver openings provided in the statue area are providing the smoke free area in 40’ level to 80’ levels and the tenability conditions of temperature of less than 60 C & visibility of more than 10 meters were maintaining from 40’ level to 140’ levels of occupancy regions.
So overall from the CFD study it can be concluded that the provided natural ventilation system is able to meet the design objective for both day to day ventilation as well as smoke ventilation modes.