Introduction
This project involves a CFD analysis of one of the potable water tanks, and the objective of the study is to optimize tank performance by analyzing water flow profiles, residence time distribution (RTD), and chlorine mixing efficiency.
Objective
The primary objectives of this CFD analysis are to achieve the following:
- Characterize the water flow profiles within the potable water tank and identify any recirculation or stagnation regions.
- Predict the residence time distribution (RTD) of the potable water tank.
- Evaluate the dispersion patterns and mixing efficiency of chlorine introduced into the tank.
- Determine whether the tank achieves plug flow conditions by calculating hydraulic efficiency indices.
Analysis and Conclusion
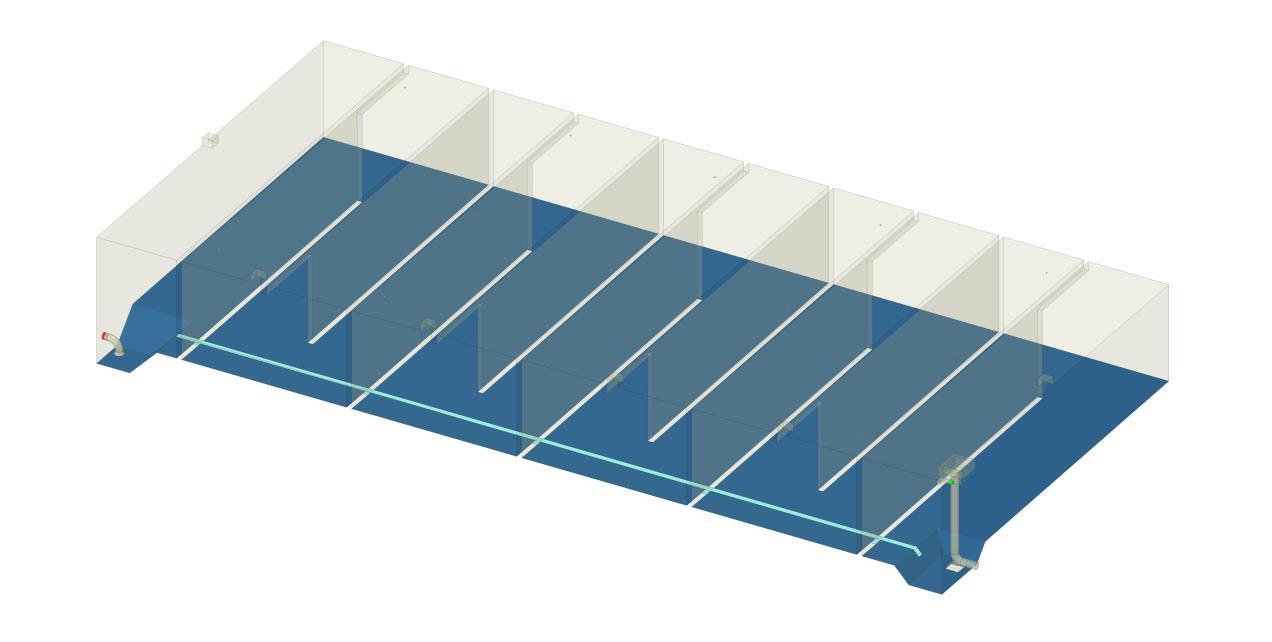
- A 3D model of the Potable water rank was developed from the 2D drawings provided and defined conditions for inlet flow rates, outlet pressures, and wall interactions to simulate real-world scenarios accurately.
- The properties of the potable water tank are specified including the density and viscosity, based on standard values
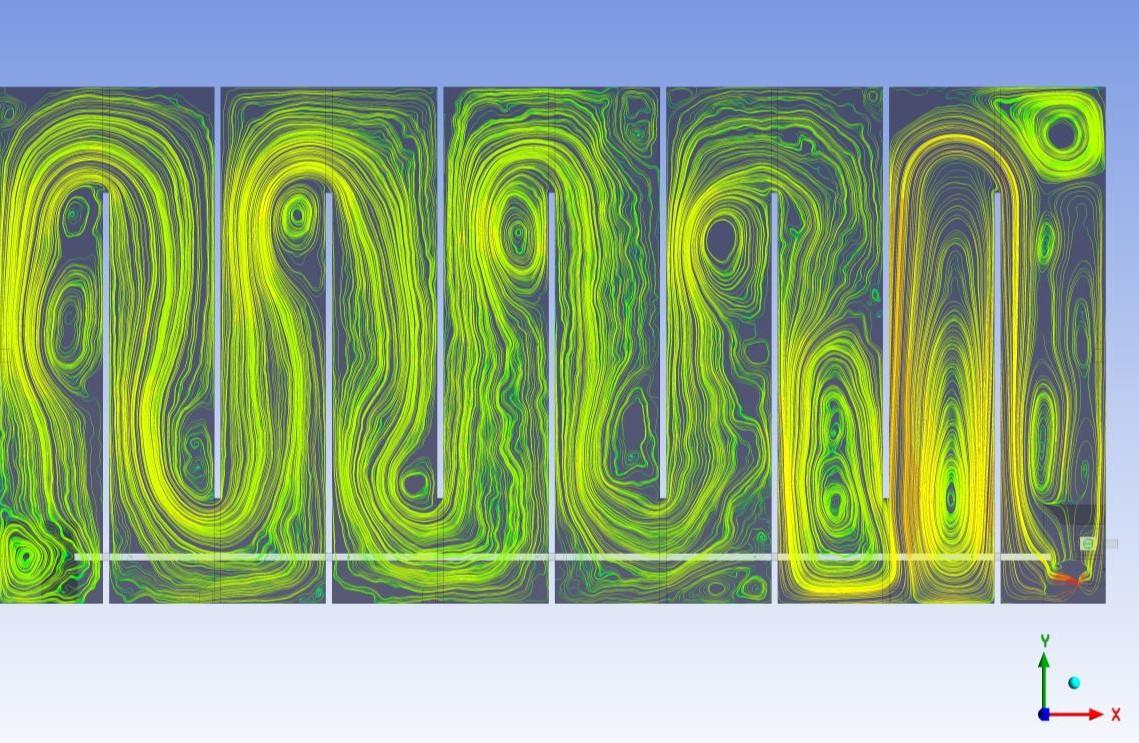
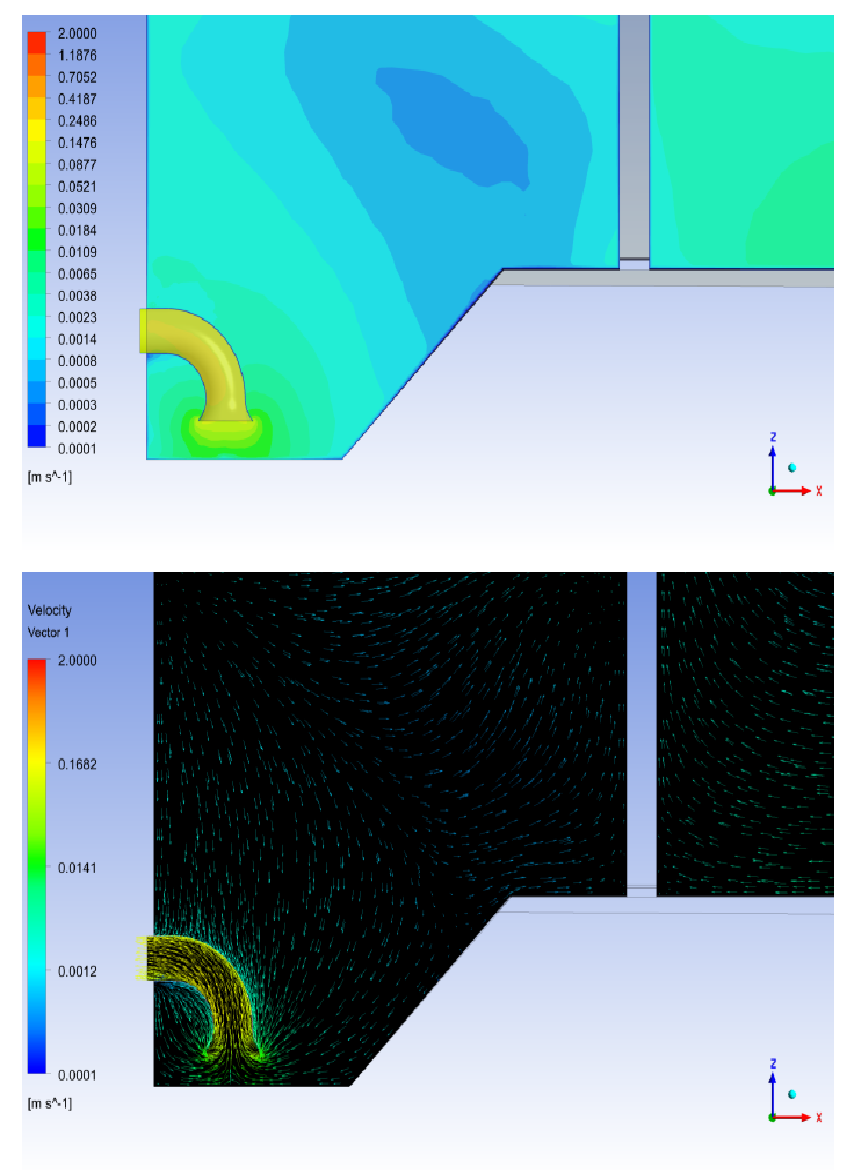
- From the study, it was observed that the flow entering the tank from the inlet nozzle is distributed through manhole openings and holes along the inlet pipe. Stagnation was also observed in the center of the tank with most of the flow at the tank boundaries.
- The mean age of the water was also calculated based on the observed CFD analysis.
- Uneven distribution of the velocities is also observed.
- Appropriate recommendations were provided including the modification requirement of the inlet arrangement and the required number of vent holes were also suggested from the CFD Study.
- Further analysis was also carried out to validate the proposed modifications and improve the design of the potable water tank.