Introduction
Anoxic tanks are critical components in wastewater treatment processes, particularly in biological nutrient removal systems. These tanks provide an environment conducive to the denitrification process, where nitrates and nitrites are converted into nitrogen gas.
Understanding the fluid dynamics within an anoxic tank is essential for optimizing its performance and ensuring effective nutrient removal. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) offers a powerful tool for simulating and analyzing the flow patterns, mixing efficiency, and overall performance of an anoxic tank.
Objective
The objective of the CFD analysis is to:
- Assess whether proper water flow circulation is occurring within the tank. This involves studying velocity profiles to understand the impact of the incoming flow and the effect of the submersible mixing pump with its four nozzles.
- Determine whether effective mixing is taking place inside the tank. This includes analyzing the Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS) or sludge concentration profiles, considering the influence of the incoming flow and the submersible mixing pump with its nozzles.
To achieve these objectives, the CFD analysis was conducted using Ansys Fluent CFD software, focusing on parameters such as velocities and MLSS/sludge concentrations.
Modeling and Analysis
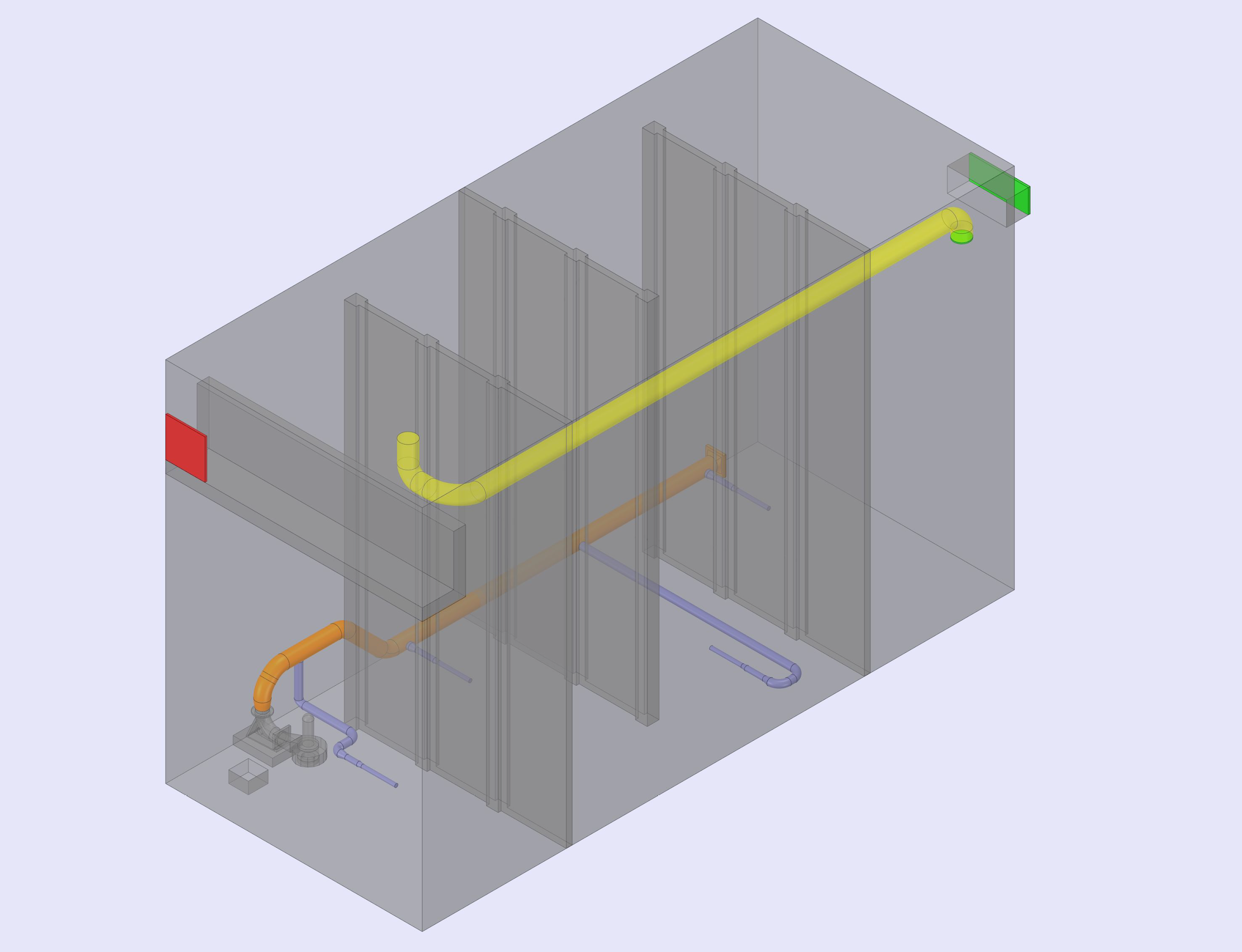
- A 3D model of an anoxic tank, including baffles, inlets, the outflow channel, and a submersible mixing pump with nozzles, was created.
- The tank has two inlets (for incoming flow and internal recirculation) and an outlet channel. The mixing pump helps ensure proper circulation and prevents sludge from settling.
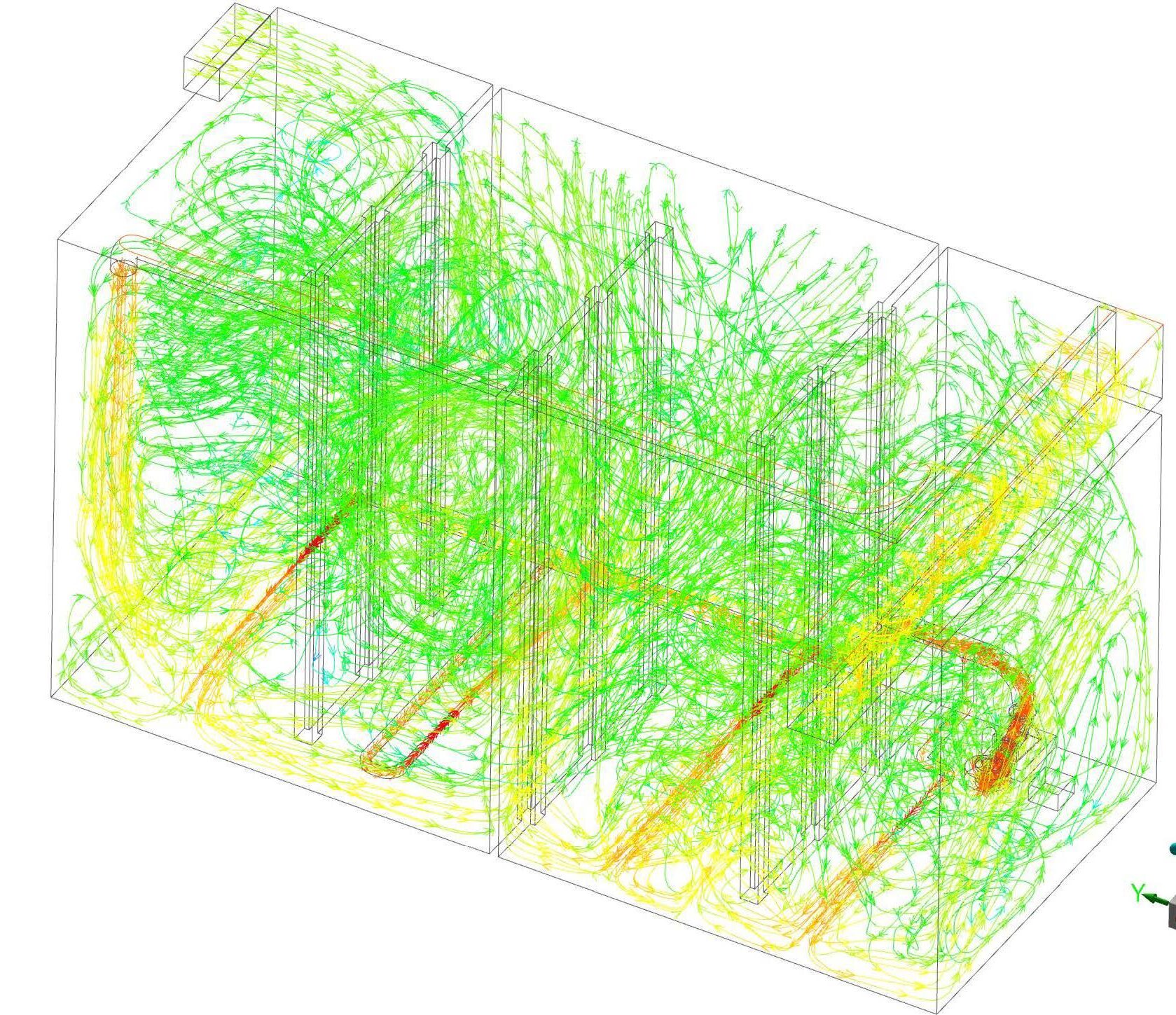
- Study the velocity profiles to check flow circulation due to the incoming flow and the mixing pump.
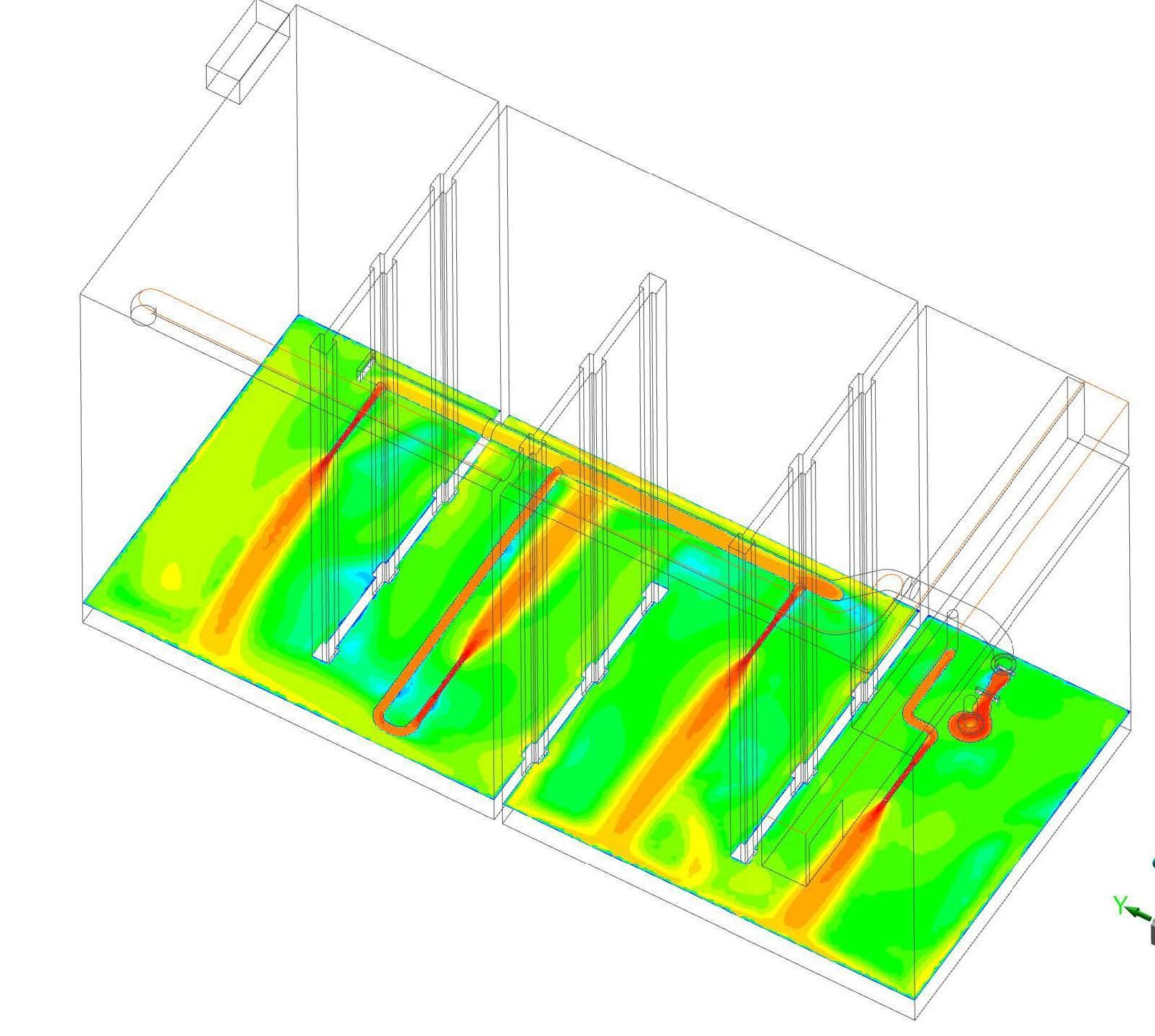
- Study the MLSS/sludge concentration profiles to evaluate mixing effectiveness and uniformity.
Conclusion
The CFD analysis confirms that the installation of the submersible mixing pump with the provided nozzles in the anoxic tank is effective in achieving proper mixing and flow circulation. Key findings include:
- The velocity profiles demonstrate that flow circulation is adequate throughout most of the tank, with effective movement and mixing.
- The MLSS/sludge concentration profiles show that the incoming flows are well-mixed before reaching the first baffle, and the concentration remains consistent throughout the tank. No significant accumulation of high MLSS/sludge concentrations at the bottom or other parts of the tank was observed.
Overall, the CFD analysis validates that the design and installation of the mixing pump and nozzles are successful in providing proper mixing and preventing sludge accumulation in the anoxic tank.