When handling volatile liquids, such as crude oils, gasoline, and other petroleum products, these liquids evaporate in containers and pipelines and exert pressure.
Sometimes, in transporting and storing these liquids, pipelines, and containers are subject to unexpected temperature changes due to heat and sunlight. This causes liquids to evaporate and raise vapor pressure. Ultimately, this leads to several threats, such as explosions, fire, air pollution, and other potential damages.
That is why True vapor pressure (TVP) and Reid Vapour pressure ( RVP) are considered important parameters in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries and should be understood and measured correctly to predict the behaviors of volatile liquids and their vapor pressure.
This article will guide you through the concepts of TVP and RVP, their key differences, and their importance.
Vapor Pressure (TVP) and Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP)?
True vapor pressure (TVP) and Reid Vapour pressure ( RVP) are important terms in thermodynamics used to measure liquids’ volatility.
Understanding them and their difference is crucial for anyone who is involved in the production, transportation, and handling of volatile liquids, such as gasoline, ethanol, and other petroleum products.
True Vapour Pressure
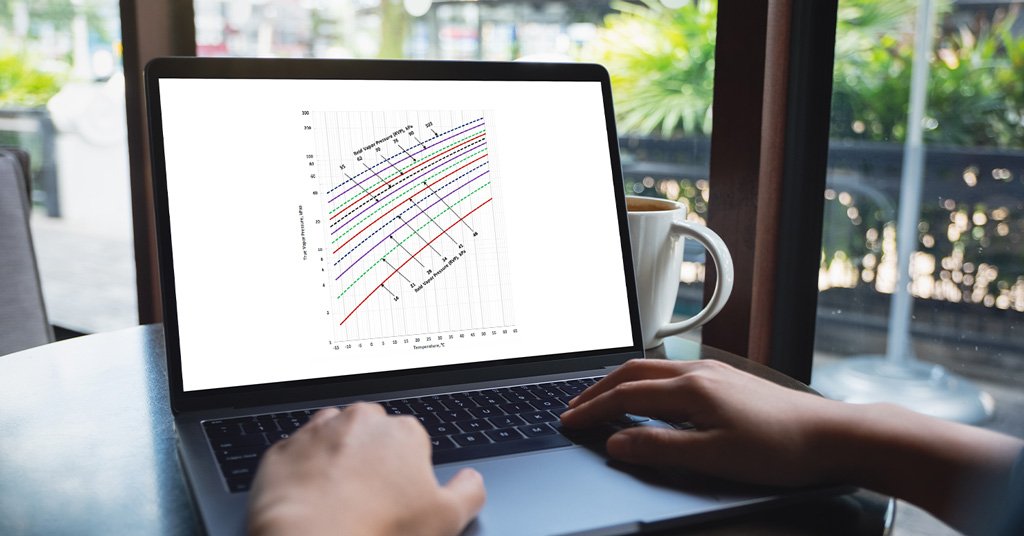
True vapor pressure (TVP) of liquids is the pressure exerted by the gasses evaporated from them in a closed container at a given temperature and in a thermodynamic equilibrium state of liquids and their gasses.
TVP predicts volatile liquid’s behavior during storage, transportation, and handling and regulates safety requirements. Also, the relationship between TVP and temperature can vary for different liquids and the factors such as purity and pressure.
The following are the steps of measurement of the TVP of a liquid.
-
Pour the liquid into a container, put it into an oven, and set the temperature to the temperature you want to measure TVP.
-
Let the liquid equilibrate to the desired temperature for a particular time.
-
Connect the pressure gauge or manometer to the container.
-
Read and record the pressure the liquid’s vapor exerts at the desired temperature.
These are the basic steps that are taken to measure the TVP of a liquid, but they can vary depending on the different methods and requirements of testing standards.
Reid Vapor Pressure

Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP) is the pressure exerted by gasses evaporated from gasoline and petroleum substances in a closed container, measured at a given temperature, such as 100 °F.
RVP is a measure of the ability of gasoline substances to evaporate at high temperatures and is also used to determine the chemical composition of gasoline blends.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the RVP of gasoline to control evaporative emissions and emissions from combustion engines to protect the environment and public health.
American Society for Testing Materials (ASTM) D323 standard provides a method for measuring RVP of gasoline and other petroleum substances. This method is used in petroleum industries and is considered a standard way of measuring RVP.
The steps of the ASTM method are as follows:
-
Fill a container with a liquid which you are going to measure the volatility of
-
Seal the container and put it into a vapor pressure apparatus.
-
Heat the container to 100 °F (37.8 °C). for a specified amount of time and apply pressure to the container using a pressure gauge.
-
Read and record the vapor pressure in the container at 100 °F/ 37.8 °C and at 1.42 bar of pressure.
Difference Between TVP and RVP
True vapor pressure (TVP) and Reid Vapour pressure ( RVP) are both used to measure the volatility of liquids, but they are not interchangeable.
There are some significant differences between both parameters, such as:
-
The significant difference between True Vapor Pressure and Reid Vapor Pressure is the temperature at which the pressure is measured. TVP is measured at room temperature, while RVP is measured at 100 °F.
-
TVP can be used with volatile liquids, whereas RVP is used only with gasoline and petroleum substances.
What Are the Importance of TVP and RVP?
True vapor pressure (TVP) and Reid Vapour pressure ( RVP) are significant parameters in petrochemical industries, environmental science, and public health and safety.
Some of the reasons why they are important are as follows:
Volatility
Volatility is the tendency of a liquid to evaporate, and it can significantly impact the environment, public health, etc. TVP and RVP offer helpful insight, such as the vapor pressure of a liquid under certain conditions. These insights can provide ways to prevent adverse impacts of the vapor pressure.
Safe Storage and Transportation
TVP and RVP can be used to predict the behavior of liquid and vapor pressure under certain conditions during transportation and storage. If the liquid is likely to evaporate, it will cause vapor pressure in pipelines and storage tanks, leading to leaks, cavitation, fire, and explosion. But it can be predicted and prevented with the help of TVP and RVP.
Environmental Regulations, Health, and Safety
TVP and RVP are used by agencies, such as Environmental Protection Agencies, to control air pollution caused by the volatility of liquids such as petrol and other substances.
Conclusion
True vapor pressure (TVP) and Reid Vapour pressure ( RVP) are crucial parameters that provide information about the volatility of most used liquids, namely petroleum products, and gasoline.
They are used to predict the behavior of these liquids during handling, storage, and transportation. Agencies, such as EPA, regulate them to control air pollution and ensure safety.
At Mechartes, we provide exceptional engineering and simulation services, such as CFD and FEA, for a variety of industries, namely, HVAC, power, gas, buildings construction, etc.
We are also leading experts in piping analysis of every kind, such as pipe stress analysis, hydraulic analysis, surge analysis, root cause analysis, and many more.
Talk to us to learn more!

 Share
Share  facebook
facebook